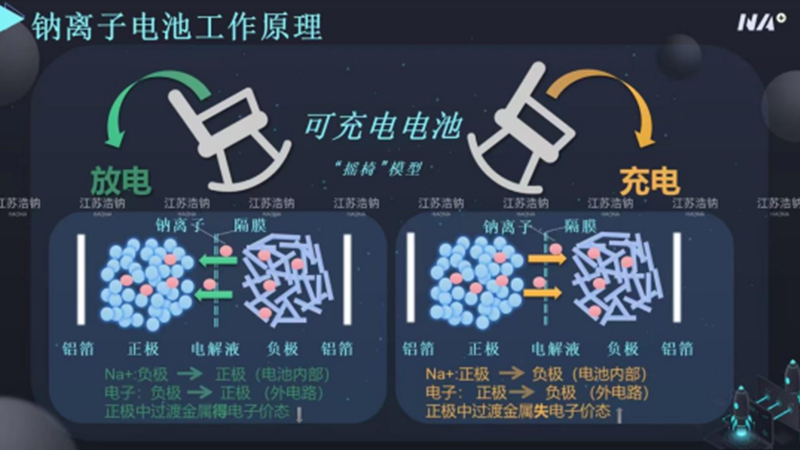
Jiangsu Haona New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. has conducted research on some high-end cutting-edge sodium ion battery technologies. Our developed negative electrode free sodium ion battery has an energy density of up to 500wh/kg, a composite collector was manufactured using atomic layer deposition method, and sodium ions can be uniformly and smoothly deposited on the surface of the collector. At the same time, soft elastic design is adopted to ensure close contact between the internal structure of the battery during the deposition and stripping process of sodium ions.
At the same time, the company has studied solid-state sodium ion batteries, which have good safety performance and can pass needle testing. The energy density can reach up to 450Wh/Kg, and the cycle time can reach over 2000 times. The use of sulfide solid electrolyte with high conductivity and strong adaptability ensures that the battery can have good rate performance like conventional liquid batteries. At the same time, artificial SEI technology and 3D sodium negative electrode technology are used to ensure the interface stability between sodium metal and solid electrolyte, as well as to avoid the surface hole problem of conventional sodium ion solid Shenchi negative electrode.
In addition, the company has also conducted research on the technology of manufacturing sodium ion battery electrodes using thousands of methods and applied for invention patents. Unlike the dry mixing, cold rolling, and hot pressing processes currently used in Tongtang on the market, the present invention uses newly developed fibrosis equipment, slicing equipment, and Fule equipment. The newly developed fibrosis equipment consists of a deformable material groove and a ramming head, which can repeatedly hammer the powder. After hammering, the fibrosis of the adhesive is more thorough and the dispersion is more uniform. The fibrosis equipment finally compresses the dry powder into a high-pressure solid density material rod, which is fed by a servo motor on the slicer and cut into thin slices using a punching knife. Then, the thin sheets are squeezed onto the collector to form electrode plates. Finally, various types of sodium ion batteries and ion batteries are manufactured through processes such as wafer viewing, electrode ear soldering, packaging, baking, liquid injection, and formation.